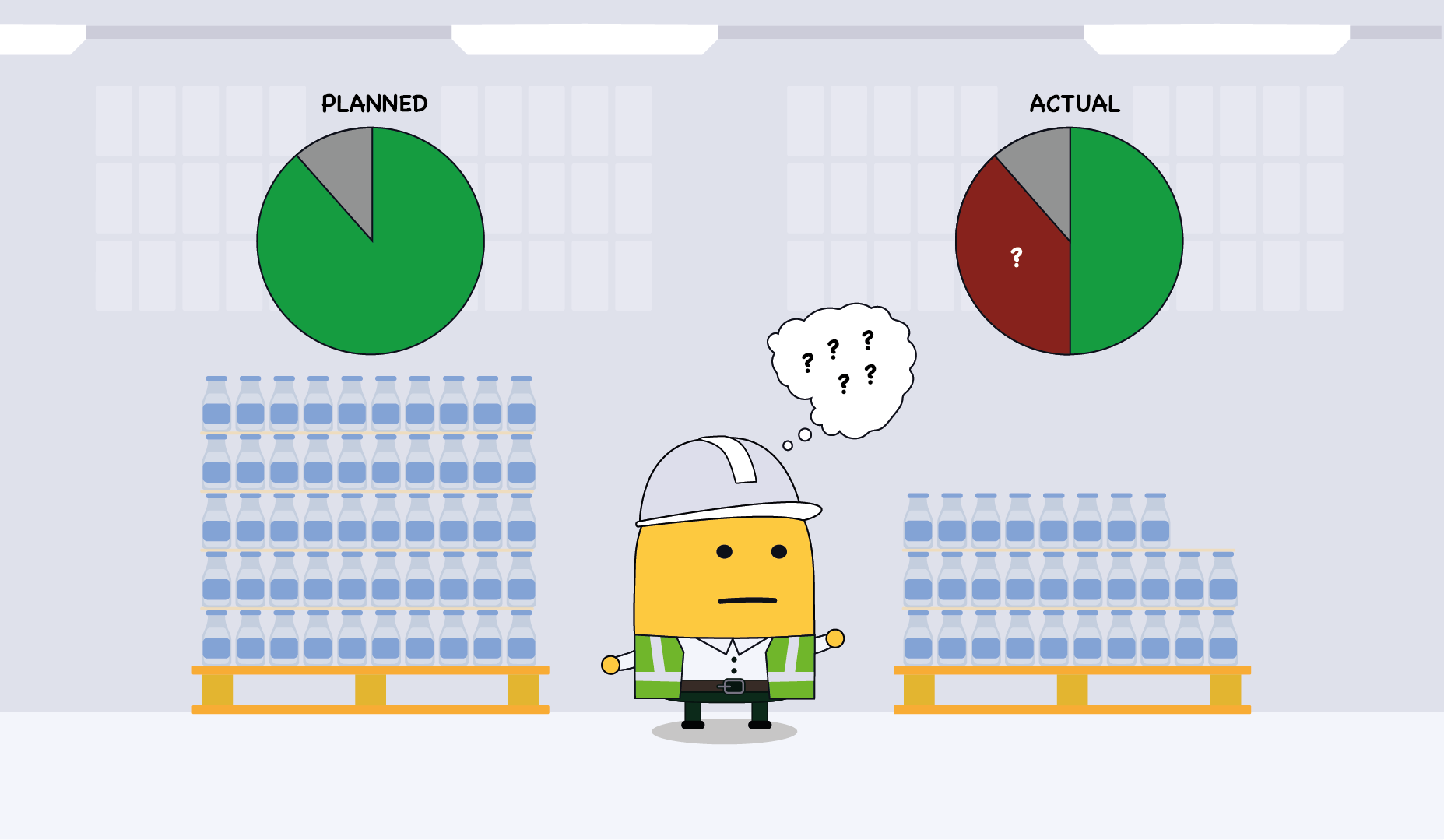
Machine utilization is one of the most vital performance indicators in any manufacturing environment. It reflects how efficiently machinery is being used by comparing the actual operating time of a machine to its available production time. This metric helps manufacturers understand whether their equipment is being used to its full potential or if there is wasted capacity. A high utilization rate often indicates efficient production planning and minimal downtime, while a low rate can signal issues such as frequent breakdowns, unnecessary idling, or poor scheduling.
Failing to monitor and optimize machine utilization can have serious consequences. When machinery is not performing at its maximum potential, it leads to increased production costs, delayed timelines, and lost revenue opportunities. This inefficiency can ripple across the entire supply chain, affecting customer satisfaction and profitability. Moreover, without accurate data on machine usage, it's difficult to make informed decisions regarding maintenance, investments in new equipment, or process improvements.
By continuously tracking machine utilization, companies gain valuable insights that can drive operational excellence. It allows for the identification of bottlenecks, preventive maintenance scheduling, and strategic resource allocation. In a competitive market, where margins are tight and customer expectations are high, improving machine utilization can be a key differentiator that helps businesses reduce waste, increase output, and boost overall productivity.
What is Machine Utilization?
In simple terms, machine utilization is a performance indicator of how well your equipment is working. Think of it like a report card for your machines. It tells you how much of the time your manufacturing equipment is actually busy making products, compared to the total time it could be running. It's a fundamental measure in any factory because machines are expensive assets, and you want to make sure you're getting the most value out of them.
A high machine utilization rate means your equipment is efficiently churning out goods, minimizing wasted time. This indicates good planning, smooth operations, and fewer unexpected stops. On the flip side, a low utilization rate is a red flag. It suggests that your machines are sitting idle too often, perhaps due to frequent breakdowns, waiting for materials, or simply not being scheduled to run at full capacity.
Understanding machine utilization is crucial because it directly impacts your bottom line. When machines aren't utilized effectively, it leads to higher production costs, missed deadlines, and ultimately, lost profits. By continuously tracking and improving this metric, manufacturers can pinpoint inefficiencies, optimize their production schedules, and make smarter decisions about their equipment investments, ensuring they stay competitive and productive.
Machine utilization is a key performance indicator in manufacturing that measures how efficiently equipment is being used. Essentially, it compares the actual time a machine spends actively producing against the total time it's available to operate. A high utilization rate is a positive sign, indicating smooth production, effective planning, and minimal idle time. Conversely, a low rate points to inefficiencies such as frequent breakdowns, unnecessary pauses, or suboptimal scheduling, all of which can lead to increased costs and missed production targets.
How to Calculate Machine Utilization
Here we have a simple machine utilization formula:
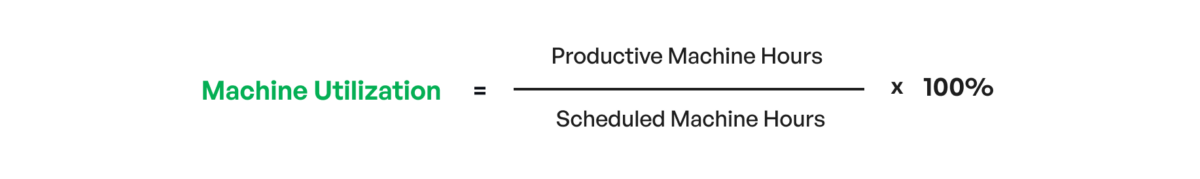
We need to know how many available hours machines are supposed to work. For our bottling line, this number is 24. What is the machine utilization if our line runs for 20 hours a day?
(20/24) *100% = 83.3%
You can run the same machine utilization calculation with your ideal and actual output/input quantities.
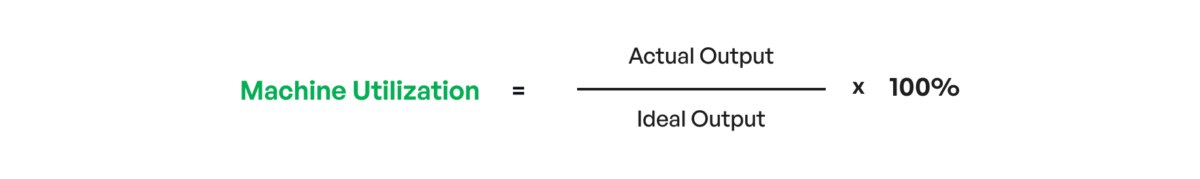
(90000/108000) *100% = 83.3%
Understanding the reasons for this 16.7% gap (losses) is crucial. The above formulas simplify a multifaceted problem in which you must consider your different machines, planned downtime, unplanned downtime, and operational inefficiencies. Below, we discuss machine utilization-related performance indicators.
How is machine utilization connected to OEE?
The connection between machine utilization and OEE is direct, and in our experience when manufacturers talk about utilization, they talk about OEE but in a simplified way. What do we mean by this?
First, we must outline that machine utilization (or asset utilization) as a KPI aims to show the gap between what you are producing and what you could be producing, in other words, the potential of your machines. Or as we stated in the beginning – how well your equipment is working. The goal of OEE is to do the same. So, both KPIs have the same goal, but where they differ is the detail level of the calculations.
The primary difference lies in the detail level of their calculations. Machine utilization typically focuses on the time aspect: how much of the available time a machine is actually running. It might not deeply differentiate between running at full speed or half speed, or producing good quality parts versus defects. OEE, on the other hand, breaks down performance into three critical components: Availability, Performance, and Quality.
By multiplying these three factors (Availability x Performance x Quality), OEE provides a much richer and more granular picture of how effectively a machine is contributing to value. While machine utilization gives a quick glance at uptime, OEE offers a deeper diagnostic tool, revealing the specific reasons for underperformance, whether it's excessive downtime (affecting utilization/availability), slow cycles, or scrap production. Therefore, OEE can be seen as a more sophisticated and comprehensive version of machine utilization, providing actionable insights for holistic operational improvement.
What time should I take as a basis to calculate my utilization?
No matter whether you are calculating machine utilization or OEE, you need to decide what time you consider your maximum potential.
If your factory must be producing 24/7, or if that is your goal, then all calendar time is available for production and, in effect, is your scheduled machine hours.
However, if your factory is meant to work 5 days a week and 24 hours each day, then that is your full potential. If you subtract holidays and other planned shutdowns or no-demand times from your schedule, then you further reduce your scheduled machine hours and then that becomes your ideal potential.
The point is to choose the time that best reflects your factory and process. There is no reason to use all calendar time to calculate your utilization (or OEE) if that is not realistic. Make a choice that best reflects your production process and helps you unlock your factory’s potential.
Ways to Improve Machine Utilization
What is a good machine utilization rate?
Perfection is almost impossible to reach in manufacturing. Often, efficiency is more about ‘good enough’ than ‘absolutely perfect.’ Machine utilization is no different than any other KPI. Acknowledging that 100% machine utilization is virtually impossible, a utilization rate above 70% indicates smooth operations and good margins.
How to improve machine utilization
Like any other KPI, there are ways to improve machine utilization. To do so, factory managers must know what happens with their machinery and act accordingly. Here is a basic checklist of actions to undertake to improve machine utilization.
The first step in improving machine utilization and production quality in manufacturing is to know your current machine utilization rates. Once you have gathered the necessary information, you know your machines performance during productive hours against scheduled hours. The data you collect will give you a baseline to inform future decisions.
In many companies, manual tracking and paper-based records are time-consuming and prone to mistakes. In addition to taking time, individuals can’t detect minor problems in production or issues within the machine.
Automated systems designed for machine utilization tracking ensure data accuracy and transparency through features such as live OEE data. Tracking OEE can determine how well you are utilizing your manufacturing equipment and identify areas that require improvement.
Modern and well-maintained machines will likely have fewer downtimes due to repairs, replacements, or other issues. Such machinery will boost productivity, as it can work longer with minimal human intervention. Furthermore, modern machines have the capability to record their downtime and the main reasons. You can collect this data in the production monitoring software of your choice making it easier to analyze the data.
Unplanned maintenance is one of the limiting factors of optimum machine utilization. Unfortunately, unscheduled maintenance is common when you rely only on operators and supervisors to track production. The good news is that if you acted as per points 1 and 2 of this checklist, you wouldn’t need to worry about it: an automated system can help prevent unplanned maintenance times easily and avoid under- or over-maintenance. This way, you can factor in maintenance when scheduling productive machine hours.